Electron microscopy Cell & Tissue
Unit info
The modern ultrastructural analysis is extremely important for the study of cancer biology. Electron microscopy (EM) has a very high resolution and is able to observe structures not visible under the light microscope. For example, the evaluation of the role of exosomes (or exovesicles) in tumorigenesis, the study of the function of oncogenes and their role in cellular organization and function. Only EM is able to find invisible under the light microscope morphological alterations induced by knock down or knock out of several oncogenes.
At IFOM we have the whole spectrum of methods suitable for the study of above problems. Our unit can perform not only routine transmission and scanning EM, but also all kinds of immune EM, correlative light electron microscopy (CLEM), three-dimensional EM (3DEM), quantitative stereological evaluation of data and so on. For instance, we can label cells using cryo-sections or using pre-embedding methods with nano-gold labelling and subsequent gold enhancements and then estimate the quantitative parameters of the cell examined. We have also developed several methods such as the video CLEM ideal for quickly moving organelles, the discretized rotator for stereological analysis and several new methodology of sample preparation for 3DEM, and so on.
In future we plan to improve methods of CLEM and 3DEM, to develop new quantitative analysis approaches based on absolute stereological estimators. Within this context, several new methods of sample preparation will be proposed in order to meet the specific demands of the researchers in IFOM. The final goal of our effort is to define a new set of guidelines for the use of modern electron microscopy in the specific field of oncology.

Coordinator
Galina Beznusenko
Photogallery
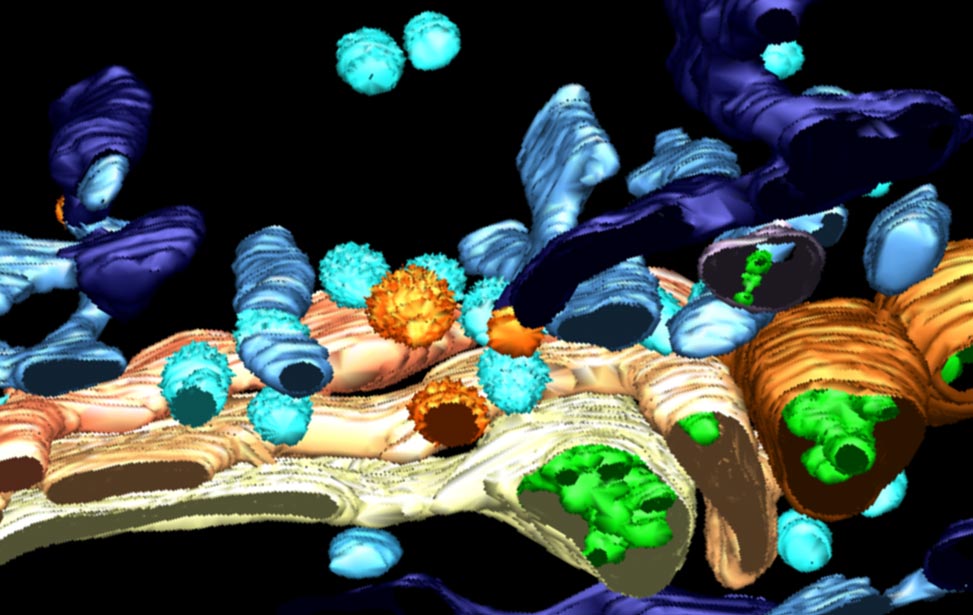
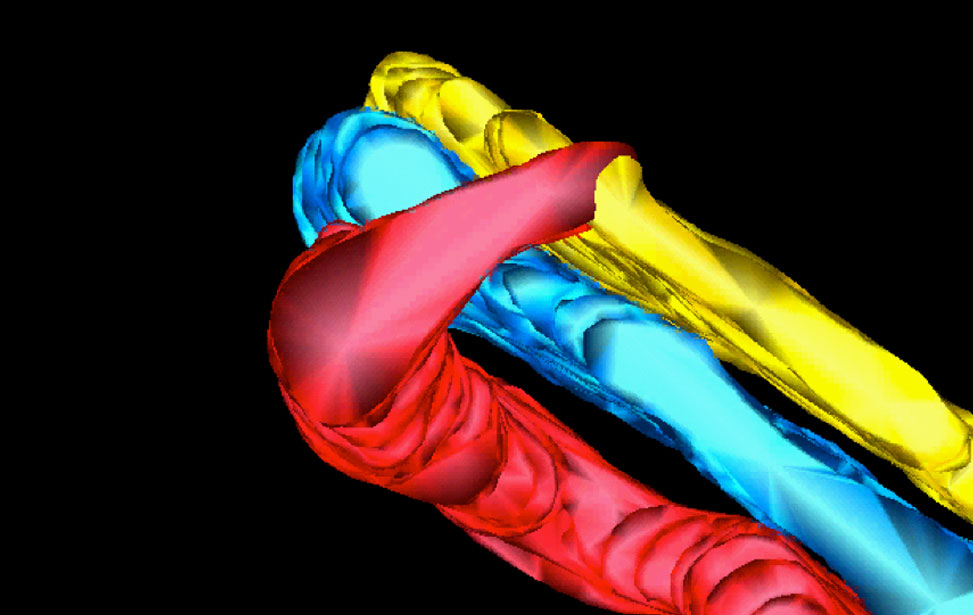 3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus
3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus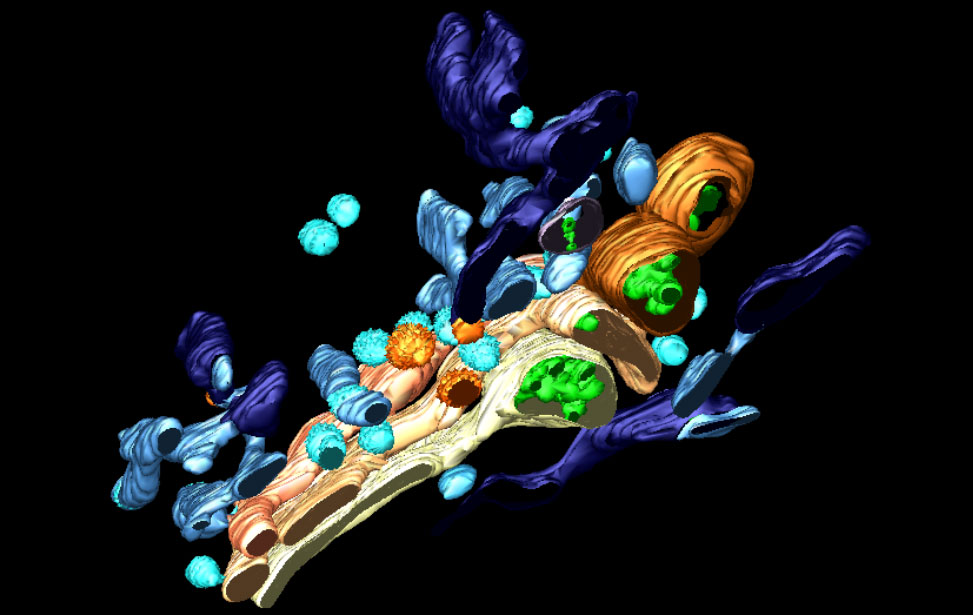 3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus
3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus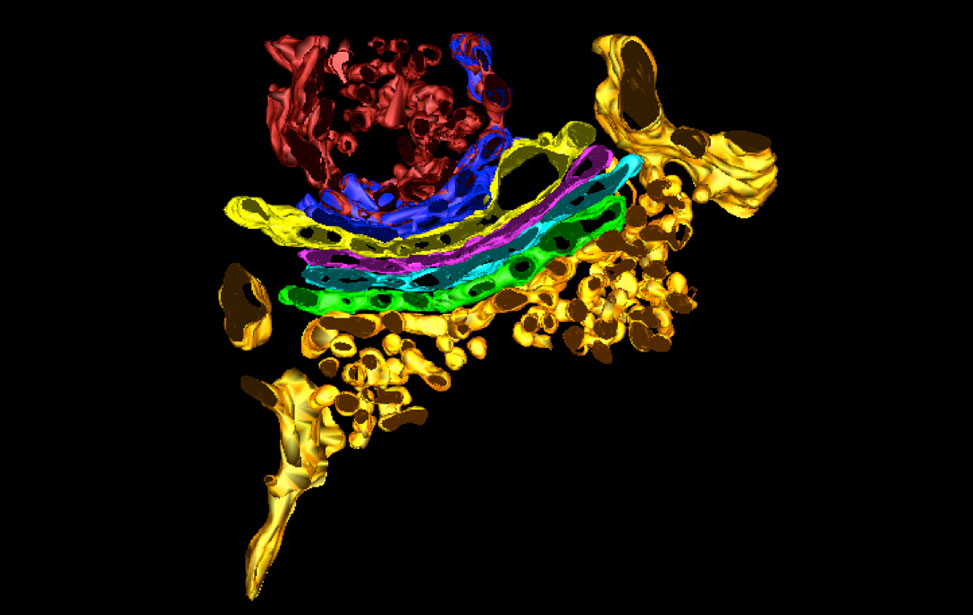 3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus
3D reconstruction of Golgi apparatus